Acne Keloidalis Nuchae: What It Is, What Are Causes, And How To Treat
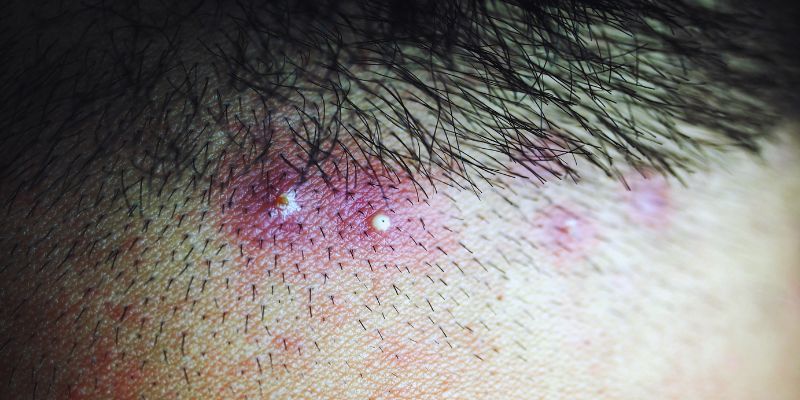
Acne Keloidalis Nuchae (AKN) is a disorder that affects the back of the neck and the nape of the head. It causes the growth of uncomfortable, itching lumps that could mimic ingrown hairs or acne. These lumps might develop into keloidsthin, elevated scars. Common in men, AKN can also afflict women, especially those with curly hair.
Although the disorder is sometimes confused with ordinary acne, its etiology and course of therapy differ somewhat greatly. This article will discuss the causes of acne Keloidalis nuchae and possible treatment choices, including specialized shampoos, lotions, and other approaches.
What Is Acne Keloidalis Nuchae (AKN)?
Acne Keloidalis Nuchae is an uncommon dermatological disorder mainly affecting the hair follicles in the neck area. The disorder causes red, inflammatory pimples that resemble those of acne at times. Still, the irregularities are usually more resistant to standard acne treatments. AKN results from inflammation of hair follicles producing nodules or pustules. These lesions might grow into keloidsbig, thick, elevated scarsover time.
AKN usually affects those with curly or coarse hair, and it causes ingrown hairs more commonly in certain hair types. People with dark complexions also more often have AKN. The bumps' unpleasant and itching nature could cause discomfort and self-consciousness.
Causes of Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
Though the precise origin of Acne Keloidalis Nuchae is unknown, various elements help to explain its development. The following are the key triggers and causes related to AKN.
- Hair Follicle Inflammation: AKN results mostly from inflammation of the hair follicles. Ingrown hairs, that is, hair that grows back into the skin instead of upward, often set off this inflammation. It irritates the skin and induces a foreign body reaction, which produces pimples and bumps.
- Shaving and Tight Collars: Cutting or shaving hair in the neck area might aggravate the hair follicles, raising the AKN risk. Headwear or tight collars could also aggravate follicles and cause ingrown hairs. Constant rubbing or pulling of the hair can establish conditions favorable for keloid development.
- Genetics: Genes also influence the development of AKN. People with certain skin typesespecially those with dark complexionsare more likely to have the disorder. Furthermore, those with a family history of keloid development are more prone to develop AKN.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes, such as those brought on by puberty, or other phases of life, may raise a person's risk of AKN. These alterations can disrupt the hair growth cycle, increasing the frequency of ingrown hairs and inflammation.
- Excessive Sweating: Too much sweating, especially in the neck area, might aggravate Acne Keloidalis Nuchae. Sweat may block pores, irritate the skin and cause more inflammation and scarring.
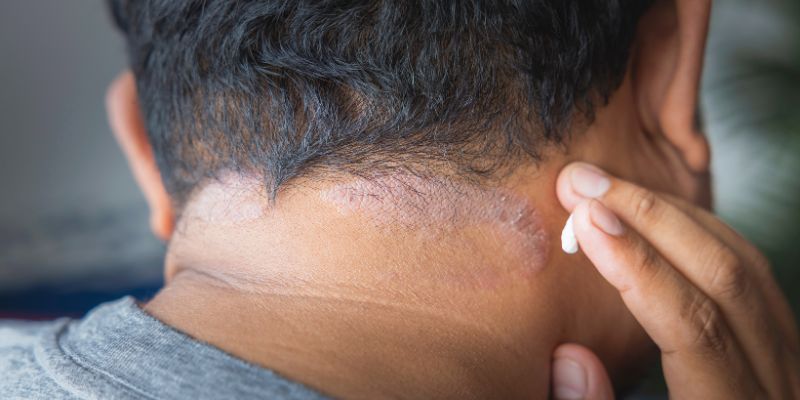
How to Treat Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
Although Acne Keloidalis Nuchae can be challenging to treat, numerous treatments are available. Many times, treatment calls for both active remedies meant to lower inflammation and scarring and preventative steps. We will go over some of the most often-used treatmentsshampoos, creams, and other techniquesbelow.
Medicated shampoos for AKN
Managing Acne Keloidalis Nuchae depends much on medicated shampoos. Many times, these shampoos have components that aid in lowering inflammation, avoiding follicle blockages, and maintaining the cleanliness of the scalp and neck area. Among the most powerful components in AKN shampoos are:
- Salicylic acid: Salicylic acid is a popular component in shampoos for treating scalp disorders. It exfoliates the skin and removes dead skin cells and waste that could block hair follicles.
- Tea Tree Oil: Renowned for its antibacterial qualities, tea tree oil can help lower inflammation and destroy the germs possibly causing keloids and pimple development.
- Ketaconazole: This antifungal component helps to control scalp infections and lower scalp inflammation, preventing AKN flare-ups.
Frequent usage of these medicated shampoos can help to lessen the frequency and severity of acne-like lumps on the head's nape and neck.
Creams and Topical Treatments for AKN
Apart from shampoos, topical creams and ointments have great power to heal pimples and stop additional keloid development. Among popular, topical treatments are:
- Corticosteroid Cream: These lotions are usually recommended to lower inflammation and swelling. They can be used directly on the afflicted region to aid in reducing symptoms.
- Retinoid Creams: Tretinoin and other topical retinoids can help hair follicles avoid clogging. They encourage cell turnover, thereby helping to avoid blockages, including ingrown hairs.
- Silicone Gel Sheets: Silicone gel sheets can help flatten the scar tissue and gradually shrink the keloid size for already-formed keloid scars.
Other Treatment Options
Although Nuchae shampoos and lotions are helpful for many people with acne keloidalis, other treatment choices should be considered.
- Laser Treatment: Laser treatment, including fractional CO2 lasers, can break down scar tissue and improve the appearance of keloids. Furthermore, laser treatment could lower inflammation in the afflicted location.
- Steroid injections: Keloids can be treated and inflammation lowered by steroid injections. Usually, a dermatologist presents these injections.
- Surgical Excision: Severe cases may require a dermatologist to advise surgically removing the keloid tissue. But surgery runs the danger of scarring and occasionally aggravates the problem.
- Avoiding Triggers: You should not shave, wear tight collars, or participate in activities that can aggravate the skin. Correct grooming and looser clothes can reduce flare-ups.
Prevention Tips for Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
Better still than treatment is prevention. Although totally avoiding Acne Keloidalis Nuchae can be difficult, there are many options you can take to reduce your risk:
- Avoid Shaving: Try not to shave the neck area; this will raise your chance of ingrown hairs. Should you have to shave, do it in the direction of hair using a razor with a guard.
- Wear Loose Clothing: Other items like tight collars and caps might irritate the skin by rubbing against it. Choose looser wear to prevent friction.
- Keep the Area Clean: Wash your neck often to prevent sweat, dirt, and oil from clogging hair follicles. Use mild cleaning products, and steer clear of strong chemicals.
- Moisturize Regularly: Maintaining skin moisture helps one prevent dryness and irritation. Moreover able to calm the skin and lower irritation are moistening creams and oils.
Conclusion:
Though it can be a chronic and annoying disorder, acne keloidalis nuchae can be managed with appropriate therapy and scarring is minimized. Medicated shampoos, topical creams, and other treatments assist in reducing inflammation and advancing recovery. If you have AKN, see a dermatologist to discuss the best course of action. Acne Keloidalis Nuchae can be managed, and the condition of your skin will improve with careful attention.